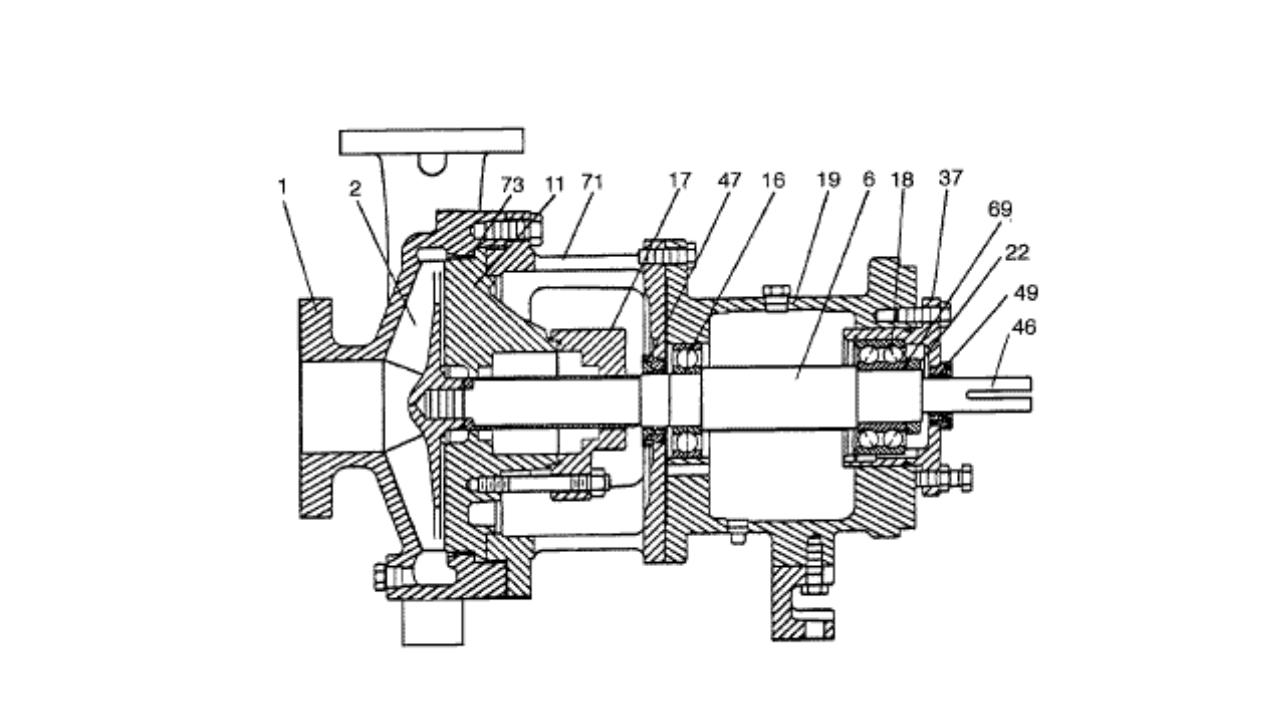
Gear Pump Operation and Maintenance
PumpScout
Gear pumps are the most common type of positive displacement pump, ideal for transferring high viscosity fluids such as automotive oils, plastics, paint, adhesives, and soaps. They operate by creating suction at the inlet with a rotating assembly of two gears –a drive gear and an idler. Flow is determined by the size of the cavity (volume) between gear teeth, the amount of slippage (reverse flow), and the speed of rotation (rpm) of the gears.
As with any pump, proper operation and regular maintenance are vital to reducing costly pump repairs and maximizing pump efficiency. Below are helpful tips for operating your gear pump and ensuring it achieves a long operating life through regular maintenance.
Gear Pump Operation
– Operate close to the maximum rated speeds. Because gear pumps have poor volumetric efficiency at low speeds and low flow rates, they should be operated as close as possible to their maximum rated speeds for higher production and efficiency.
– Use special materials when pumping liquids with abrasives. A pump’s toothed gear construction allows particles to become trapped in small spaces, accelerating wear and reducing efficiency. If you need to transfer fluid containing abrasives, consider contacting the pump manufacturer to discuss hardened material options.
– Ensure that total life does not exceed 7.5 PSI. A gear pump cannot create a perfect vacuum, necessitating total lift (including pipe friction losses) to be one-half of the atmospheric pressure (approximately 7.5 PSI).
– Avoid low viscosity fluids. Gear pumps (especially internal gear pumps) are designed to handle high viscosity fluids to minimize slip. Pumping low viscosity fluids results in reduced flow rate and efficiency because it ‘slips’ through the tight spaces from the higher-pressure discharge side of the pump to the lower-pressure suction side of the pump.
– Do not run dry. Unlubricated gear teeth will rub together, creating friction and heat as the cogs expand and begin rubbing against the housing. This can destroy the pump, requiring costly repair and downtime.
Gear Pump Maintenance
– Keep maintenance records. One of the most important things you can do to ensure your pump operates smoothly is to keep a detailed record of baseline pump performance, regular maintenance, and any repairs. This will aid you in determining how the pump will operate in the future and the best way to either repair or replace specific parts.
– Check bearings regularly. The bearings are the most important area to maintain because they can cause imbalance if misplaced or defective. Check bearings regularly and replace as necessary by removing the defective bearing with a puller. Excessive noise can be an indication of bearing wear.
– Check gear pump clearance. A new gear pump has .007 to .005 inches of clearance from both the teeth and chamber of the gears. Periodically check for wearing of the teeth by attempting to pass a piece of paper between the clearances. If it passes between the clearances easily, it indicates that the bearings have been worn down and should be replaced.
By following regular maintenance schedules and adhering to proper operation procedures, gear pumps can be an efficient and productive solution to high-viscosity pumping needs.
PumpScout
Related Articles
Oh "Overall Equipment Effectiveness", I've heard about that before! Unfortunately, in many facilities, that's all OEE (Overall Equipment Effectiveness) is to the personnel. Something they heard of, talked about or read about. Many maintenance departments today still do not effectively utilize the OEE tool even though it's widely used among the world class companies.
Oh "Overall Equipment Effectiveness", I've heard about that before! Unfortunately, in many facilities, that's all OEE (Overall Equipment Effectiveness) is to the personnel. Something they heard of, talked about or read about. Many maintenance departments today still do not effectively utilize the OEE tool even though it's widely used among the world class companies.
See More
Contrary to popular opinion, a centrifugal pump is not designed to develop one head at a single capacity as requested by the pump purchaser. In fact a pump is designed and produced to supply a whole range of head-capacity conditions as identified on it’s performance curve. The pump will operate on that curve if it is driven at the particular speed for which the curve is drawn.
Contrary to popular opinion, a centrifugal pump is not designed to develop one head at a single capacity as requested by the pump purchaser. In fact a pump is designed and produced to supply a whole range of head-capacity conditions as identified on it’s performance curve. The pump will operate on that curve if it is driven at the particular speed for which the curve is drawn.
See More
Ask for a modern centrifugal pump recommendation from your favorite supplier and chances are he will recommend one of the standard pump designs that conform to either the A.N.S.I., I.S.O. or D.I.N. specifications. On the surface that might seem like a good recommendation, but the fact is that all of these designs will cause you maintenance problems. Refer to the illustration prior to diving into the details of the obvious problems found within these designs.
Ask for a modern centrifugal pump recommendation from your favorite supplier and chances are he will recommend one of the standard pump designs that conform to either the A.N.S.I., I.S.O. or D.I.N. specifications. On the surface that might seem like a good recommendation, but the fact is that all of these designs will cause you maintenance problems. Refer to the illustration prior to diving into the details of the obvious problems found within these designs.
See More
It's important to find out if material flows are present or not throughout a bulk-processing facility; material cost savings and increased plant efficiency can offset an investment in monitoring. Most bulk solids processors can do this using low-cost acoustic emission-monitoring technology.
It's important to find out if material flows are present or not throughout a bulk-processing facility; material cost savings and increased plant efficiency can offset an investment in monitoring. Most bulk solids processors can do this using low-cost acoustic emission-monitoring technology.
See More
For optimum chain drive performance the following points should be considered when looking at chain drive design.
For optimum chain drive performance the following points should be considered when looking at chain drive design.
See More
The most common question asked by seal salesmen is "what are you sealing?" This is usually followed by asking about shaft size, product, temperature, speed, stuffing box pressure and any other operating conditions they can think of. The problem with this simplistic approach is that you would have to have a very large data bank of information to reference a particular problem so as to be able to make a sensible seal recommendation. There is a much more logical approach to the problem that we will be discussing in the following paragraphs.
The most common question asked by seal salesmen is "what are you sealing?" This is usually followed by asking about shaft size, product, temperature, speed, stuffing box pressure and any other operating conditions they can think of. The problem with this simplistic approach is that you would have to have a very large data bank of information to reference a particular problem so as to be able to make a sensible seal recommendation. There is a much more logical approach to the problem that we will be discussing in the following paragraphs.
See More
Sizing electric motors correctly for hydraulic power units can save a sizable amount of money over the life of the equipment. If system pressure and flow are constant, motor sizing simply boils down to the standard equation: hp = QP / 1714EM
Sizing electric motors correctly for hydraulic power units can save a sizable amount of money over the life of the equipment. If system pressure and flow are constant, motor sizing simply boils down to the standard equation: hp = QP / 1714EM
See More